The fiber optic cable color code is a universal system that helps identify different fibers, tubes, and jackets within optical cables. Each color represents a specific position or function. This system keeps networks organized and reduces connection errors during installation and repair. Learning these colors is key for anyone working with fiber optics.
Understanding the Basics of Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optics changed how information travels across the world. Instead of carrying data as electrical signals like copper cables, fiber uses pulses of light to move information quickly and clearly. These light beams bounce along strands of glass thinner than a human hair, reaching miles without losing signal strength.
A fiber optic cable is not just one fiber. Inside each cable are bundles of strands protected by coatings and jackets. When dozens or hundreds of these fibers are packed together, knowing which strand connects where becomes difficult. That’s where the fiber optic color code becomes essential.
It’s more than just color it’s communication. Every shade has a meaning, helping engineers, splicers, and network designers keep track of each connection. Without color coding, maintenance and upgrades would become confusing and risky.
Why Color Coding Matters in Fiber Optic Connections
Imagine hundreds of identical fibers lying side by side. Without distinct colors, one wrong connection could take hours to trace. The fiber optic cable color code prevents that chaos. It provides a clear, visual way to identify each strand and maintain organized systems.
For example, a blue fiber always represents the first position in a bundle, orange the second, and so on. This repeatable pattern helps installers know instantly which strand they are working with. When new lines are added or old ones repaired, the color system makes it easy to find the right match.
Color codes also improve efficiency. Projects finish faster because technicians don’t have to label every strand manually. It saves time, reduces stress, and ensures precision, especially in large commercial or telecom installations where hundreds of fibers run through a single cable.
What the Fiber Optic Cable Color Code Represents
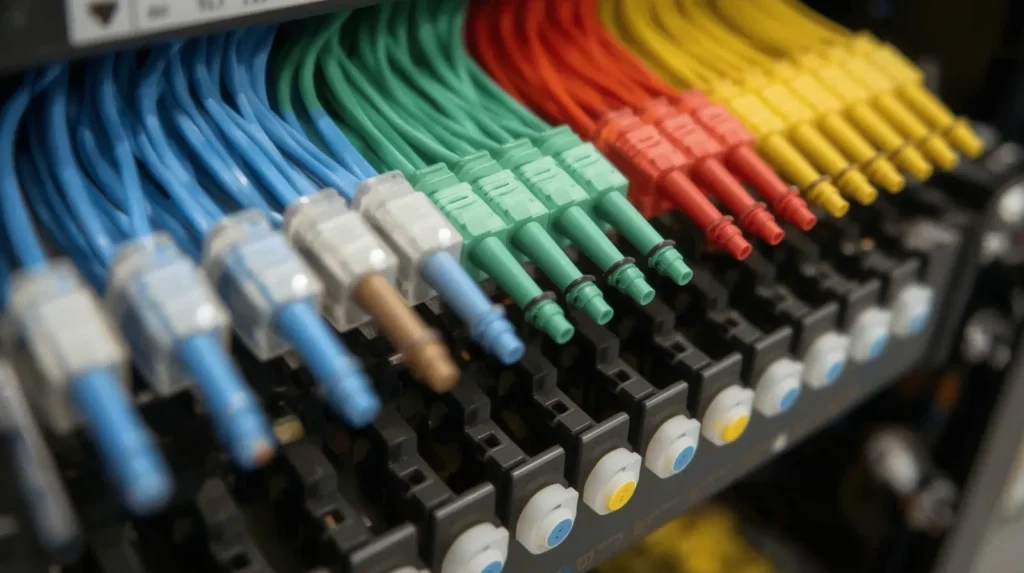

At first glance, the color sequence may seem decorative. In reality, it’s a powerful organizational tool. Each color marks a specific fiber’s position in the bundle and its corresponding terminal point.
The standard color pattern starts like this:
- Blue
- Orange
- Green
- Brown
- Slate (gray)
- White
- Red
- Black
- Yellow
- Violet
- Rose (pink)
- Aqua
After twelve fibers, the pattern repeats but within another tube or layer. For example, if there are 24 fibers, there will be two sets of these twelve colors. This repetition continues up to hundreds or even thousands of fibers in large network systems.
Understanding these sequences ensures smooth installations, accurate splicing, and proper documentation. It’s one of the first things any fiber technician must master.
The Standard Optical Fiber Color Coding System
The optical fiber color coding system is governed by the TIA-598 standard, developed to make color identification consistent across the industry. Before this standard, manufacturers used different color schemes, which led to confusion during repairs and installations.
Now, whether a project takes place in Dallas, Dubai, or Tokyo, the same pattern applies. This standardization ensures global compatibility and simplifies training.
The TIA-598 defines not only fiber strand colors but also buffer tube and jacket colors. Here’s how it works:
- Single-mode fibers: Usually have yellow outer jackets to show that they handle long-distance, high-bandwidth connections.
- Multi-mode fibers: Typically use orange, aqua, or lime green jackets. These handle shorter runs and local networks.
This makes identification instant. When a technician opens a panel and sees a yellow jacket, they know they’re dealing with single-mode fiber.
12-Strand and 24-Strand Fiber Color Codes Explained
The 12-strand color sequence is the foundation of all larger cable designs. For a 12-strand fiber, the colors progress from blue to aqua as described earlier. Each color corresponds to a fiber number, which helps during splicing or termination.
When moving to 24-strand cables, the sequence repeats. The second set is often marked with a stripe or dash to show it belongs to the next group. In even larger cables such as 48, 96, or 144 fibers these groupings repeat inside color-coded tubes.
For example, the first 12 fibers may be housed in a blue tube, the next 12 in an orange tube, and so forth. This layered organization makes it easier to locate specific fibers even in massive networks.
Technicians who understand this pattern can splice faster, troubleshoot smarter, and avoid mix-ups that can disrupt entire systems.
Decoding Multi-Mode Fiber Color Identification

Multi-mode fiber color identification helps distinguish between different performance types. The jacket colors tell you the fiber’s grade and intended use:
- Orange: Common for OM1 and OM2 multi-mode fibers used in short-distance links.
- Aqua: Represents OM3 or OM4 fibers that support higher speeds like 10Gbps and 40Gbps.
- Lime green: Used for OM5 wideband fibers designed for next-generation networks.
This color coding makes network management easier, especially in large facilities where multiple fiber types coexist. A quick glance can reveal which cable supports high-speed data and which serves standard connections.
Multi-mode fibers allow several light paths inside the core, making them ideal for data centers, office buildings, and schools. Single-mode fibers, on the other hand, carry light through one straight path, making them perfect for long-distance communication.
How to Read Fiber Ribbon and Buffer Tube Colors
When cables hold hundreds of fibers, it’s not enough to color each strand. That’s where buffer tubes and ribbons come in. Each tube contains a group of fibers, and these tubes follow their own color code sequence too.
For example:
- The first tube is blue.
- The second is orange.
- The third is green.
- The fourth is brown, and so on.
Inside each tube, the fibers again follow the 12-color pattern. This dual coding—tube color plus fiber color—creates a precise coordinate system. A fiber can be identified as “tube three, fiber seven,” meaning the seventh fiber in the green tube.
Fiber ribbon cables work similarly. They pack fibers side-by-side into flat ribbons. Each ribbon follows the same sequence, repeating after every 12 fibers.
This structure helps technicians handle high-count cables efficiently and ensures accurate mapping during installation or repair.
Visual Guide to Optical Fiber Color Charts

A fiber optic color chart is an essential reference in every technician’s toolkit. It visually displays all color sequences for strands, tubes, and jackets.
Here’s a quick snapshot of common chart segments used in the field:
- Fiber strands: Blue, orange, green, brown, slate, white, red, black, yellow, violet, rose, aqua.
- Buffer tubes: Follow the same pattern but apply to groups of fibers.
- Jackets: Yellow for single-mode, orange or aqua for multi-mode.
Charts can also include extended versions for 24, 48, 72, or 144 fibers. Large-scale projects often require laminated charts on-site to help crews cross-check fiber numbers and prevent confusion.
Technicians working on complex systems use color charts as quick visual guides to confirm their work before splicing or testing. It’s a small but powerful tool that keeps large networks running smoothly.
Common Mistakes in Fiber Splicing Color Code Identification
Even experienced technicians make mistakes during splicing. The most frequent one is mismatching fibers by color. When blue connects to orange, data signals can fail completely.
Another common error is skipping documentation. Without proper labeling or charts, future repairs become difficult. Over time, these small oversights cause confusion, wasted hours, and signal interruptions.
To prevent this, always:
- Verify every color before fusion splicing.
- Use a fiber splicing color code chart nearby.
- Label every completed connection clearly.
- Keep records for future maintenance.
Patience and accuracy matter more than speed. Every strand carries critical information, and even one wrong connection can cause downtime for an entire building or network.
Practical Uses of Fiber Optic Color Codes in Dallas, TX Networks
At Heritage Cabling, precision is everything. We use the fiber optic cable color code system for all structured cabling and data network projects throughout Dallas, TX. Whether it’s a corporate office, data center, or multi-building campus, color-coded fibers ensure quick installation, easy troubleshooting, and consistent performance.
Our technicians follow both TIA-598 and EIA standards, guaranteeing accurate splicing, labeling, and long-term reliability. We also teach clients how to read their own network diagrams and color codes for future maintenance.
By keeping every strand traceable, we help businesses avoid confusion when expanding or upgrading their fiber systems. Organized color coding means faster service, fewer errors, and a smoother communication experience for everyone.
Choosing the Right Experts for Fiber Optic Installation
Fiber optic work demands more than just technical skill it requires attention to detail and a commitment to precision. Every splice, connector, and color sequence must align perfectly for data to flow without loss.
Heritage Cabling brings years of hands-on experience in fiber installation, testing, and maintenance. Our certified team handles projects of all sizes with the same level of care and professionalism. We use top-grade materials, follow industry standards, and document each step of the process.
When choosing a contractor, look for one that values accuracy, transparency, and ongoing support. An experienced company not only installs your cables but also ensures you understand your network layout. That builds long-term trust and reliability.
Contact Heritage Cabling today for expert fiber optic installation, maintenance, and network design services. Our skilled team will make sure your fiber system is built to perform at its best and grow with your business ne